AI 聊天機器人市場大洗牌:ChatGPT 市佔率暴跌 20%,Gemini 異軍突起,Claude 5 即將登場
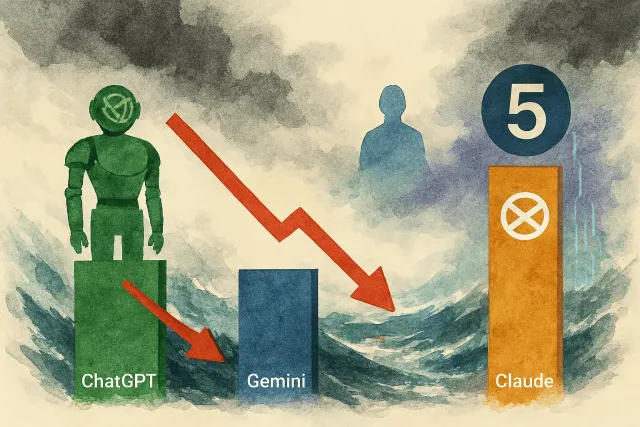
2026 年 AI 聊天機器人市場迎來劇烈變化。ChatGPT 從 87% 跌至 68%,Google Gemini 飆升至 18%,Anthropic 傳聞即將發布 Claude Sonnet 5。三巨頭競爭白熱化,獨佔時代正式結束。

2026 年 AI 聊天機器人市場迎來劇烈變化。ChatGPT 從 87% 跌至 68%,Google Gemini 飆升至 18%,Anthropic 傳聞即將發布 Claude Sonnet 5。三巨頭競爭白熱化,獨佔時代正式結束。

2026 年 2 月是遊戲大月。Nioh 3(2/6)、Dragon Quest VII Reimagined(2/5)、惡靈古堡安魂曲(2/27)等重磅作品接連發售。本文整理完整發售清單與購買建議。

Elon Musk 的 xAI 推出 Grok 3,號稱在數學、科學、編程基準測試中超越 ChatGPT 與 DeepSeek。本文深入解析 Grok 3 的核心功能、實際表現與適用場景。

Capcom 的《惡靈古堡 安魂曲》是系列第九款正傳作品,首次採用雙主角設計。新角色 Grace 主打生存恐怖,老將 Leon 主打動作戰鬥。本文整理所有已知情報。

Team Ninja 的《仁王 3》即將在 2 月 6 日發售,帶來全新的武士/忍者雙流派系統、開放區域探索、德川家光的戰國故事。本文整理所有已知情報,幫你決定是否入手。

世界模型正成為 2026 年 AI 技術的核心戰場,Google、NVIDIA、Meta 等科技巨頭紛紛投入,目標是打造能理解現實世界的 AI 系統,推動自駕車、機器人、虛擬實境等領域的突破。
從固定對白到動態情緒與記憶系統,2026 年的 AI NPC 正在改寫遊戲敘事。這篇文章解析它們如何影響玩家體驗、遊戲設計,以及未來幾年的發展方向。

AI 不再只是陪聊。2026 年是自主 Agent(Autonomous Agents)爆發的一年。本文解析 Agent 與 Chatbot 的關鍵差異,以及它如何自動化你的繁瑣工作。

OpenAI 宣布在 ChatGPT 測試廣告功能,免費和 Go 用戶將看到廣告。本文詳解廣告機制、隱私保護、用戶反應,以及這對 AI 產業的影響。

《噬血代碼 2》(Code Vein 2)於 1 月 30 日正式發售,帶來時空穿越的全新劇情、開放世界探索、搭檔系統。本文詳細評測遊戲優缺點,幫你決定是否值得入手。

Godot 4.6 已於 1 月 27 日正式登場!帶來了內建 Jolt 物理引擎、全新的反向運動學框架、Modern 編輯器主題,以及 LibGodot 嵌入式支援。這篇技術分析將帶你一覽所有關鍵更新。

《永無寧日》(No Rest for the Wicked)迎來了 2026 年首次重大更新,正式推出備受期待的多人合作模式,並帶來了全新的終局 endgame 內容「瘟疫爆發」。本篇將為您深入解析所有關鍵改動,幫助您與夥伴在薩克拉島上順利開荒。